Content

Currency from foreign countries must be translated to the reporting currency for financial reporting purposes. The conversion should provide results comparable to those that would have occurred if the business had completed operations using only one currency. Translation losses from the devaluation of foreign currency are not reported with cash and cash equivalents. These losses are reported in the financial reporting account called “accumulated other comprehensive income.” Cash and cash equivalents help companies with their working capital needs since these liquid assets are used to pay off current liabilities, which are short-term debts and bills.
Is a receivable a cash equivalent?
Accounts Receivable DO NOT fall under the category of Cash Equivalents.
The standard suggests a short maturity would be three months or less from the acquisition date. So, to qualify as cash equivalents, BAs should have a three-month or less maturity period from the acquisition date, not the reporting date. Once a company has calculated the cash balance based on these terms, it can use this information to decide how to best use its cash. For example, if the company has a positive cash balance, it may want to reinvest some of that cash into the business. Alternatively, if it has a negative cash balance, it may need to take out a loan or raise additional capital. The cash balance formula is also used to forecast future cash balances so that a company can plan its finances accordingly.
Industry considerations for CCE
Should the investment mature after three months, it’s recorded as “other investments” on the balance sheet. Many companies have foreign bank accounts or have bank accounts in other countries, especially if they are doing a lot of business in those countries. A company’s foreign currency is translated and reported in Canadian dollars at the exchange rate at the date of the balance sheet. Cash and cash equivalents information is sometimes used by analysts in comparison to a company’s current liabilities to estimate its ability to pay its bills in the short term. However, such an analysis may be excessively conservative if there are receivables that can be readily converted into cash within a few days; in this case, receivables should also be included in the analysis.
Commercial paper is also very liquid since it can be traded on a secondary market and is quickly converted into cash. The interest rate on commercial paper varies depending on the creditworthiness of the issuing firm. In short, cash and cash equivalents are a firm’s most liquid short-term assets. The assets considered as cash equivalents are those that can generally be liquidated in less than 90 days, or 3 months, under U.S. Cash equivalents are short-term investments that can be easily liquidate, carry low risk of loss, and have active marketplaces to ensure quick transacting.
Cash Equivalents Examples and Formula
To help users assess solvency, the balance sheet reports the balance of cash and cash equivalents. A negative cash and cash equivalents balance shows that a company’s cash outflows exceed its cash inflows and lacks enough cash reserves to pay its short-term commitments and obligations. Cash and cash equivalents are generally used by businesses to settle invoices and current portions of long-term debts when they are due. Such obligations are usually due within a short timeframe and require immediate payment.
What are examples of cash equivalents?
- Treasury bills.
- Treasury notes.
- Commercial paper.
- Certificates of deposit.
- Money market funds.
- Cash management pools.
If they have maturities of 12 months or less, they are classified as short term. In practice, the cash and cash equivalents account is excluded from the calculation of net working capital (NWC). To reiterate, the “Cash and Cash Equivalents” line item refers to cash – the hard cash found in bank accounts – as well as cash-like investments. Both a three-month U.S Treasury bill (purchased 1/15/CY and matures 4/15/CY) and a three-year Treasury Note purchased three months from maturity qualify as cash equivalents. What’s considered a reasonable number of cash and cash equivalents to have on hand varies greatly from industry to industry.
Controlling and Reporting of Cash and Receivables
These instruments can easily be converted to cash but are classified differently because they are not actual claims of ownership of cash. This is because these assets’ prices are restricted by the short-term interest rates set by centralized banks like The Federal Reserve in the U.S. So, as money market assets get closer to their maturity date, market forces will guide their prices toward set rates. Additionally, CCE contributes to working capital, in that net working capital is the difference between current assets, which includes CCE, and current liabilities. This is different from the short-term assets included in cash and cash equivalents, whose value doesn’t tend to vary very much and is more predictable.
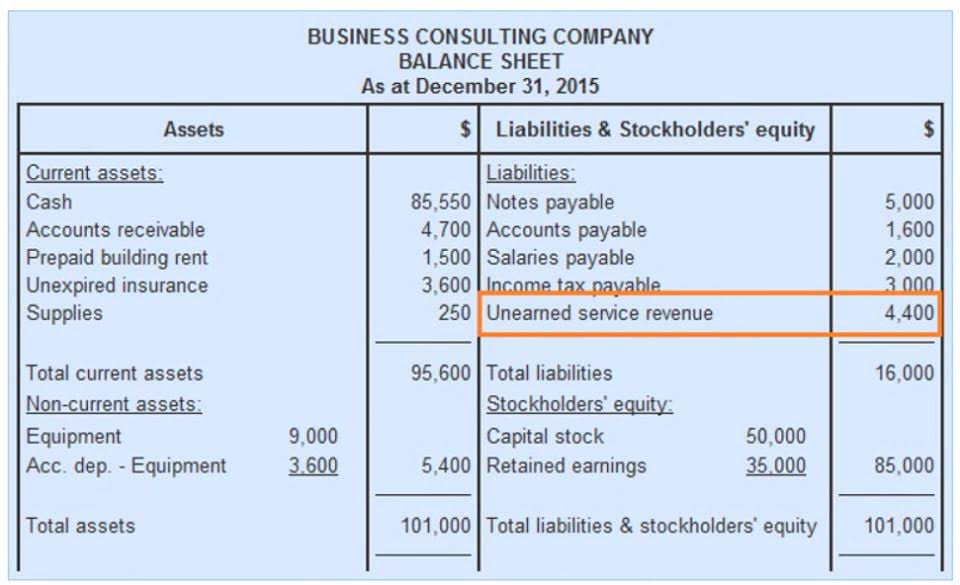
According to the acquisition strategy, we can assume that the company is not thinking of any new acquisitions in the future as they have not increased their cash reserves over 12 months. A business with a large amount of https://www.bookstime.com/articles/cash-and-cash-equivalents cash is in a better position to weather unexpected expenses or take advantage of opportunities as they arise. The goal of financial accounting for cash is the disclosure of the balance on hand at the balance sheet date.
Apple Financial Model – Cash and Cash Equivalents
Building a very strong cash position can also create pressure from shareholders to pay dividends or issue stock buybacks, which are ways of returning capital to shareholders. However, companies need to balance being prepared for short-term cash needs with using their resources wisely, to generate earnings. You can see on the top line of the balance sheet that the value of CCE fluctuates as these two factors play out in terms of higher oil and gas prices and periods of high capital expenditure. Another example is when the price of equity shares fluctuates a lot and these shares are highly liquid, ie equity shares can be redeemed into cash whenever an investor wants to.

Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as a university accounting instructor, accountant, and consultant for more than 25 years. However, this needs to be viewed in the context of the recent history and short-term future expectations for the company. Industries that are not capital-intensive, such as entertainment, media, or software firms, do not have the same spending needs as capital-intensive industries like oil, gas, or steel. A company could need cash quickly in order to cover slowing sales or another, urgent unexpected need for cash. This is very different from other markets, like the stock market, where there is no guaranteed end price for an asset.
Connect With a Financial Advisor
Also, cash is regarded as the safest and most readily liquid asset, but cash equivalents feature some risks owing to fluctuations in the market. While cash equivalents are often seen as low-risk investments, they are nonetheless vulnerable to market fluctuations and may lose value. Since prepaid assets do not reflect readily available cash, they are not regarded as https://www.bookstime.com/. Prepaid assets are types of assets that have been paid for in advance but provide benefits over time.
For the most part, cash and cash equivalents do not include equity or stock holdings because the price of those assets can fluctuate significantly in value. A note provides the breakup of the overall sum at the end of the financial statement. The cash and cash equivalent will generally bear a number beside its total, which describes the serial number in the notes section to understand the breakup of the cash and cash equivalent. As a practical matter, efficient financial management results in a very low cash balance because any excess funds are invested in cash equivalents.
What makes a financial instrument a cash equivalent?
Businesses often use their available cash or cash equivalents to fund daily operations, pay for short-term investments or purchase necessary supplies/equipment. Additionally, companies may use these funds to pay off debts and taxes or to provide reserves for unexpected situations. Cash and cash equivalents may not keep up with inflation, and exchange rate shifts may influence their value.

Cash is the ownership of money, whereas cash equivalents are the ownership of financial instruments easily converted into cash. Petty cash funds are classified as cash because these funds are used to meet current operating expenses and to pay current liabilities as they come due. Even though petty cash has been set aside for a particular purpose, its balance is not material, so it is included in the cash balance in the financial statements. The cash and cash equivalents line item on the balance sheet states the amount of cash on hand plus other highly liquid assets readily convertible into cash.
What’s Not Included in Cash Equivalents
This subject is covered in management accounting and financial management courses. Furthermore, as a regulatory requirement, maintaining cash and cash equivalents can assist in limiting systemic risks in the financial system. Cash is available for use immediately, while cash equivalents have a maturity date, generally three months or less. Accounts receivable are payments due by customers to a business for products sold or services supplied. While these funds can be expected to be collected soon, they do not count as cash or cash equivalents until they are received.
- Cash is money in the form of currency, which includes all bills, coins, and currency notes.
- Working capital is important for funding a business in the short term (12 months or less) and can be used to help finance inventory, operating expenses, and capital purchases.
- Restricted cash items should be included on the balance sheet (in cash and cash equivalents) however, in the notes to the financial statements, restricted cash should be separated with detailed explanations.
- As a practical matter, efficient financial management results in a very low cash balance because any excess funds are invested in cash equivalents.
- Generally, only investments with original maturities of three months or less meet this definition.
Cash and cash equivalents is a line item on the balance sheet, stating the amount of all cash or other assets that are readily convertible into cash. Any items falling within this definition are classified within the current assets category in the balance sheet. If there is any question about whether a financial instrument can be classified as a cash equivalent, consult with the company’s auditors.


